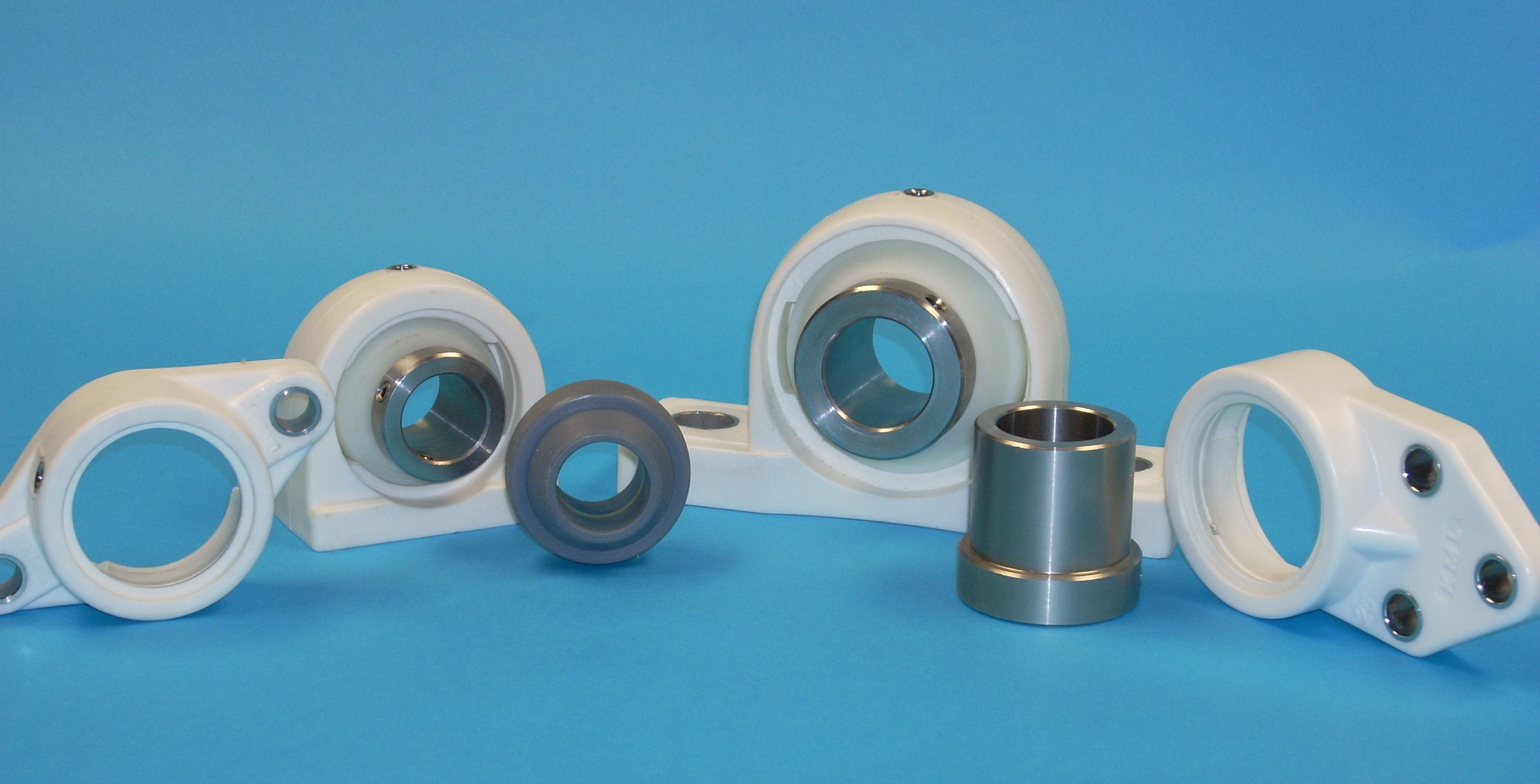
Why would you use plastic bearings and bushings? Depending on the application, choosing to use plastic over metal materials can offer exceptional advantages. Plastic bearings contribute to longer life, reduced maintenance costs, and lower energy consumption.
What are Plastic Bearings?
Plastic ball bearings are bearings built from plastics, such as nylon, acetal, and PTFE. They can be self-lubricating when combined with carbon graphite and other non-metallic materials.
These types of bearings were a necessary development to replace metallic bearings in applications with a higher risk of corrosion, electrical conduction, and magnetism.
For instance, they were not ideal for food processing, swimming pools, and applications in the medical field. Also, they can be easily machined to fit various applications and absorb shocks better than metal, since plastics are naturally elastic.
Types of Plastic Ball Bearings
1. Single-row deep grove plastic ball bearings
This type of bearing (no matter the material) has a wide range of applications. This is because they are built to withstand heavy loads and high operating speeds.
In applications where the load is both axial (acting along the shaft) and radial (acting around the side of the shaft), deep groove ball bearings have proven to be dependable. Although the amount of axial load capacity is limited. But when built of plastic, this gives a silent and smooth bearing.
2. Thrust plastic ball bearings
This is a type of rotary bearing built specifically for axial load, not radial loads. They are available as single direction or double direction thrust ball bearings and are designed to support thrust loads at high speeds. The plastic variant of thrust ball bearings makes them the best option for high-precision use.
3. Angular contact plastic ball bearings
Angular contact bearings have their bearing axis at an angle with the line of action of the load. And this load could be radial or thrust loads. But the thrust can only be in one direction. They’re ideal for high-speed applications.
4. Self-aligning plastic ball bearings
How can a plastic ball bearing be self-aligning? When its outer ring’s trajectory is spherical. The center of curvature of the bearing matches the center of the bearing. This allows the inner ring, ball, and retainer to rotate freely around the bearing center. And that’s how it aligns itself.
They can correct shaft misalignment more than any other type of plastic ball bearing and that’s what makes them popular for sophisticated devices these days.
5. Miniature plastic ball bearings
As the name suggests, they’re smaller versions of plastic bearings and are required for small diameter parts and lighter applications. Even though they’re small, they’re built to support the load they bear and perform well in high-precision equipment and applications too small for other types of plastic bearings.
Why Bearings Made of Plastic Are Cost-Saving and Durable
Most engineers and technicians don't expect plastic ball bearings to be as reliable as their metallic counterparts. But the opposite is the case. While this kind of bearing can withstand heavy loads, high-speed and high-temperature applications, they also provide corrosion resistance that helps put less pressure on maintenance teams.
And there are more advantages of plastic bearings:


 Plastics today are used in almost unlimited number of applications, many of which were previously handled by metal components, especially when the application required the part to be exposed to harsh conditions such as temperature extremes. Today’s modern plastic formulations are superior in many ways to previous generations of plastic materials; however, they come in a wide range of compounds and not all plastics are suitable for all applications. Every plastic formulation has its own unique characteristics, such as durability, tensile and impact strength, temperature range, and more.
Plastics today are used in almost unlimited number of applications, many of which were previously handled by metal components, especially when the application required the part to be exposed to harsh conditions such as temperature extremes. Today’s modern plastic formulations are superior in many ways to previous generations of plastic materials; however, they come in a wide range of compounds and not all plastics are suitable for all applications. Every plastic formulation has its own unique characteristics, such as durability, tensile and impact strength, temperature range, and more. Unlike metals or ceramics, plastics are viscoelastic materials – that is, they respond to stress as if they’re a combination of a viscous fluid and a plastic solid. In other words, while plastics have solid-related characteristics such as stability of form, strength — and, yes, elasticity — they also possess fluid-like properties such as flow, which can be affected by temperature, rate, and time as well as the amount of loading.
Unlike metals or ceramics, plastics are viscoelastic materials – that is, they respond to stress as if they’re a combination of a viscous fluid and a plastic solid. In other words, while plastics have solid-related characteristics such as stability of form, strength — and, yes, elasticity — they also possess fluid-like properties such as flow, which can be affected by temperature, rate, and time as well as the amount of loading.
 A proprietary, new high-performance
A proprietary, new high-performance